
Composed of the President and the Vice President, the cabinet, executive departments, independent agencies, and other boards, commisions, and committees.
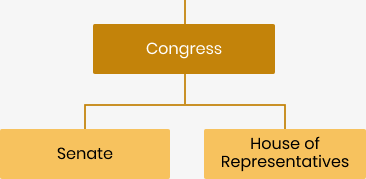

The Congress makes up the legislative branch of the government. It is composed of the Senate, also known as the upper house, and the House of Representatives known to many as the lower house. The Congress drafts, reviews, amends, and repeals proposed laws (bills). It also has the power to amend the 1987 Constitution and is tasked with passing the national budget each year.

The Judiciary is composed of the Philippine courts and the Supreme Court, the highest court of the land. Judges and Justices are appointed by the president who chooses from a pre-screened list of nominees issued by the Judicial Bar Council. The Supreme Court is composed of the Chief Justice and of the fourteen Associate Justices. The judiciary interprets the meaning of laws, applies the laws to particular cases, and decides if a law violates the Constitution.
Elections have long granted the citizens the power to change the country's status quo. With thousands of seats to be filled up in the elections, one vote can either break or change a nation.
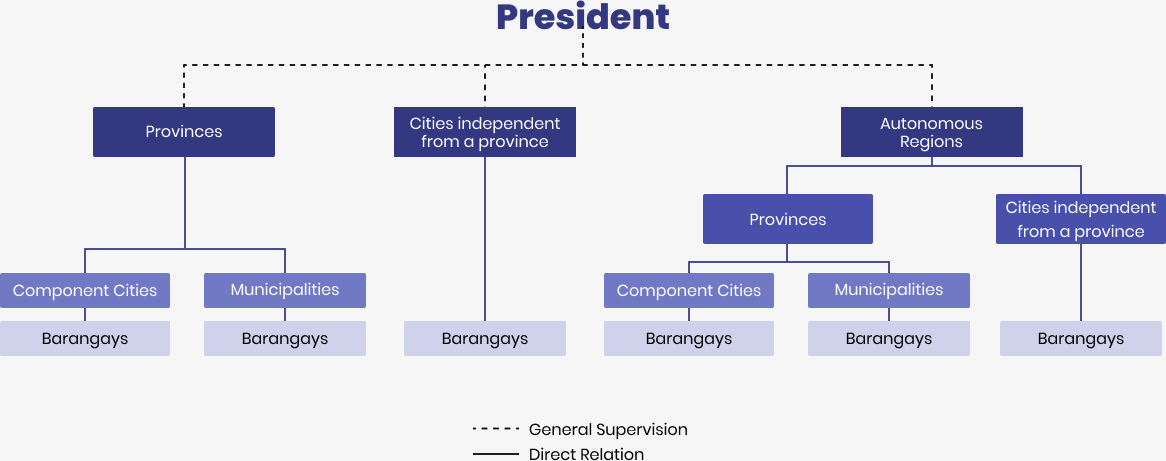
Elections take place for people to vote for executive and legislative branches of the government on a national, provincial, and local level. National elections are for putting in position a president and a vice president. National elections are also for the 12 Senate seats, 316 seats to the House of Representatives, 81 seats for governors and vice governors, and 782 seats to provincial boards in provinces. 146 seats to city mayors and vice mayors, and 1,650 seats to city councils in all cities, 1,488 municipal mayors and vice mayors, and 11,908 seats to municipal councils in all municipalities.
Strong institutions are one of the 17 Sustainable Development Goals of the United Nations, and the act of voting and appointing government officials is a right afforded to every citizen once they turn 18. They have the power to make their voices heard just by going through the process of registering.
Ultimately, choosing the right leaders who practice good governance could help drive all SDGs to attain progress and sustainability in our country.


- Prior to registration, visit www.votepilipinas.com for everything you need to know about voter registration. You can also locate the active Office of the Election Officer (OEO) near you.
- Download and fill-out the voter registration form but DO NOT sign yet. The form has to be signed in front of an election officer at the OEO.
- Go early to the OEO or registration center. Bring your own pen, face mask, vaccination card and valid IDs. Fall in line to your assigned queue (PWD, senior, pregnant, regular citizen) and submit your registration form.
- Have your biometrics captured.
- Receive your acknowledgement receipt and wait for your application to be approved by the Election Registration Board.
- Find out where to vote through COMELEC’s Precinct Finder here.
- Have your temperature checked before entering the voting center.
- Proceed to the Voters' Assistance Desk (VAD) to secure your precinct and sequence numbers and assigned room or clustered precinct.
- Go to your assigned room and introduce yourself to the Electoral Board by stating your name, precinct and sequence numbers.
- Get your ballot, ballot secrecy folder and marking pen and fill-out the ballot at the voting area.
- Accomplish the ballot by fully shading the oval appearing before the name of the candidate you wish to vote for. Do not overvote.
- Feed the ballot into the Vote Counting Machine (VCM).
- Check your voter's receipt and then deposit it in the receptacle.
- Have your right forefinger nail stained with indelible ink.
- Go to your precinct and look for the priority lane for senior citizens, PWDs, and pregnant women.
- Present a valid government ID to the facilitator.
- Wait your turn and cast your vote inside the precinct. You can bring a cheat sheet or a list of the candidates you want to vote for to make the process easier for you!
- Once you're done, go to the vote counting machine and insert your ballot. For senior citizens, persons with disabilities, and illiterate voters, headphones will be provided, so you can clearly hear and follow the VCM instructions.
- Indelible ink will be applied to your forefinger nail as proof of voting.
- Review your voter's receipt and drop it into the receipt receptacle box.
Visit the Candidate Profile Dashboard of Vote Pilipinas and help spread the word.
SIGN UP AND GET INVOLVED.